钉钉群里收到报警信息
一时找不到原因,让运维同事重启了服务器,先解决问题再定位原因。
查看阿里云ECS的监控情况
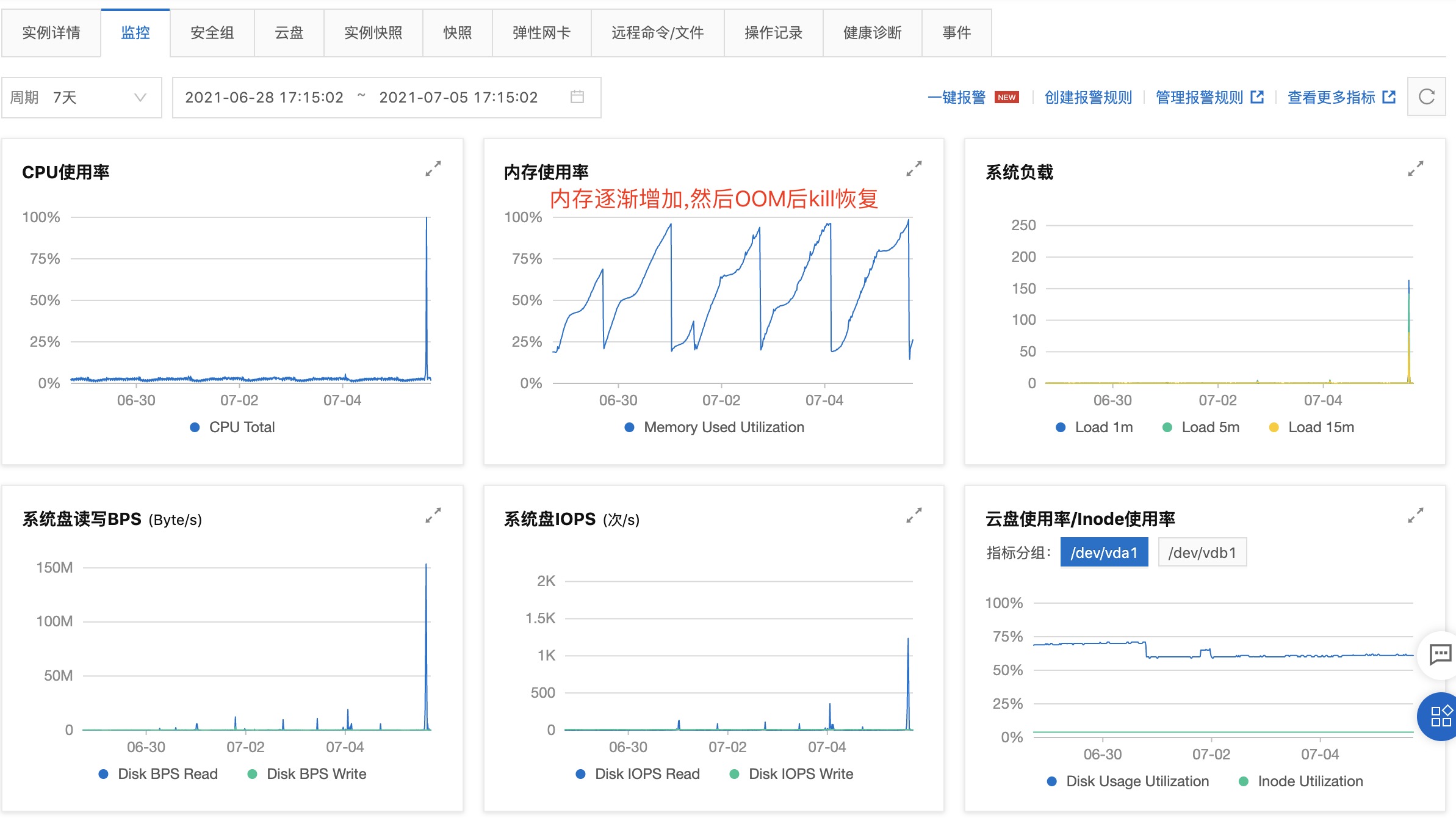
先怀疑cpu,磁盘问题,同事们回想一下最近的修改,主要是消息中心和接入阿里云的日志服务。
浏览了最近提交的一些服务的代码,没有看出异常。
重启服务器后,使用vmstat、pidstat 等性能工具,观察系统和进程的 CPU 使用率。 // 附录1
# 所有进程的 CPU 统计信息
pidstat -u 1 10
# 显示 IO 统计信息
pidstat -d
# 显示内存统计信息
pidstat -r 10 100 > pid_mem.lgo &
发现消息中心服务的内存占用不断的缓慢增加
查看系统日志,确实有oom-kill的记录
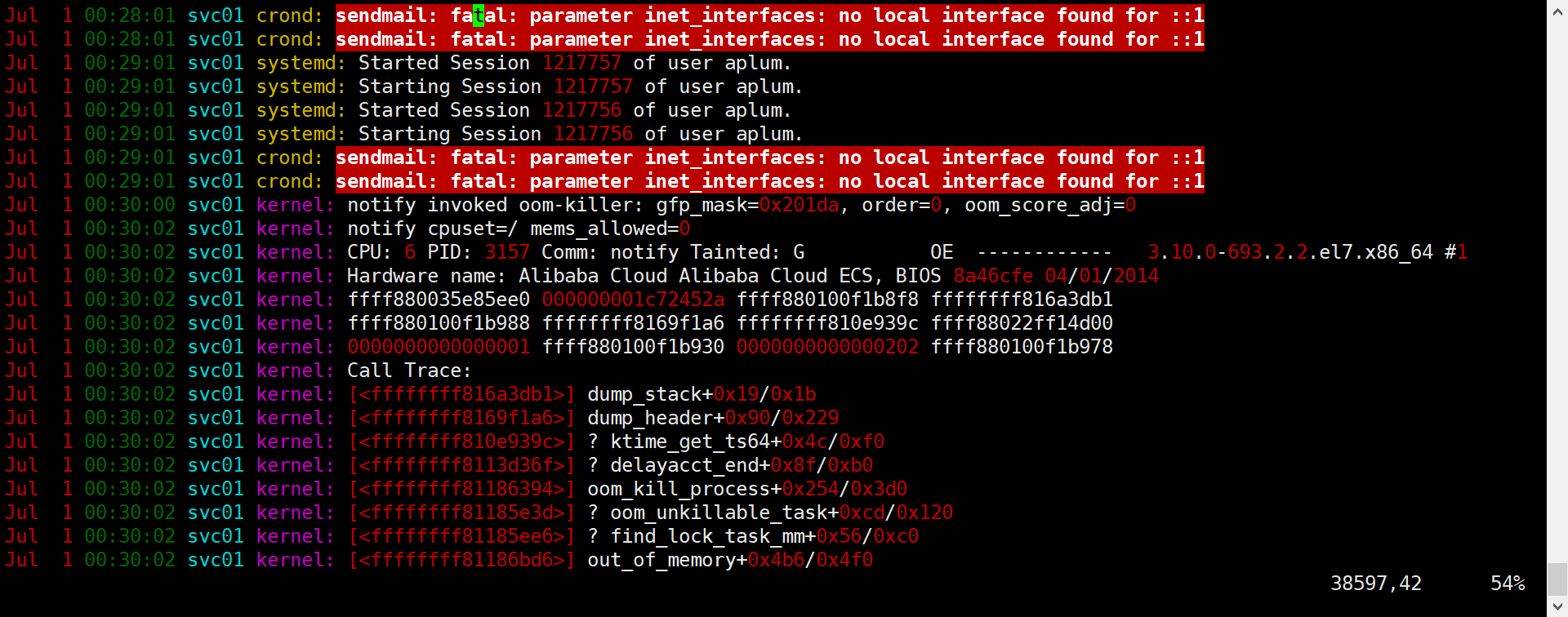
查看服务的supervisor日志
发现同一时间服务收到SIGKILL信号的重启
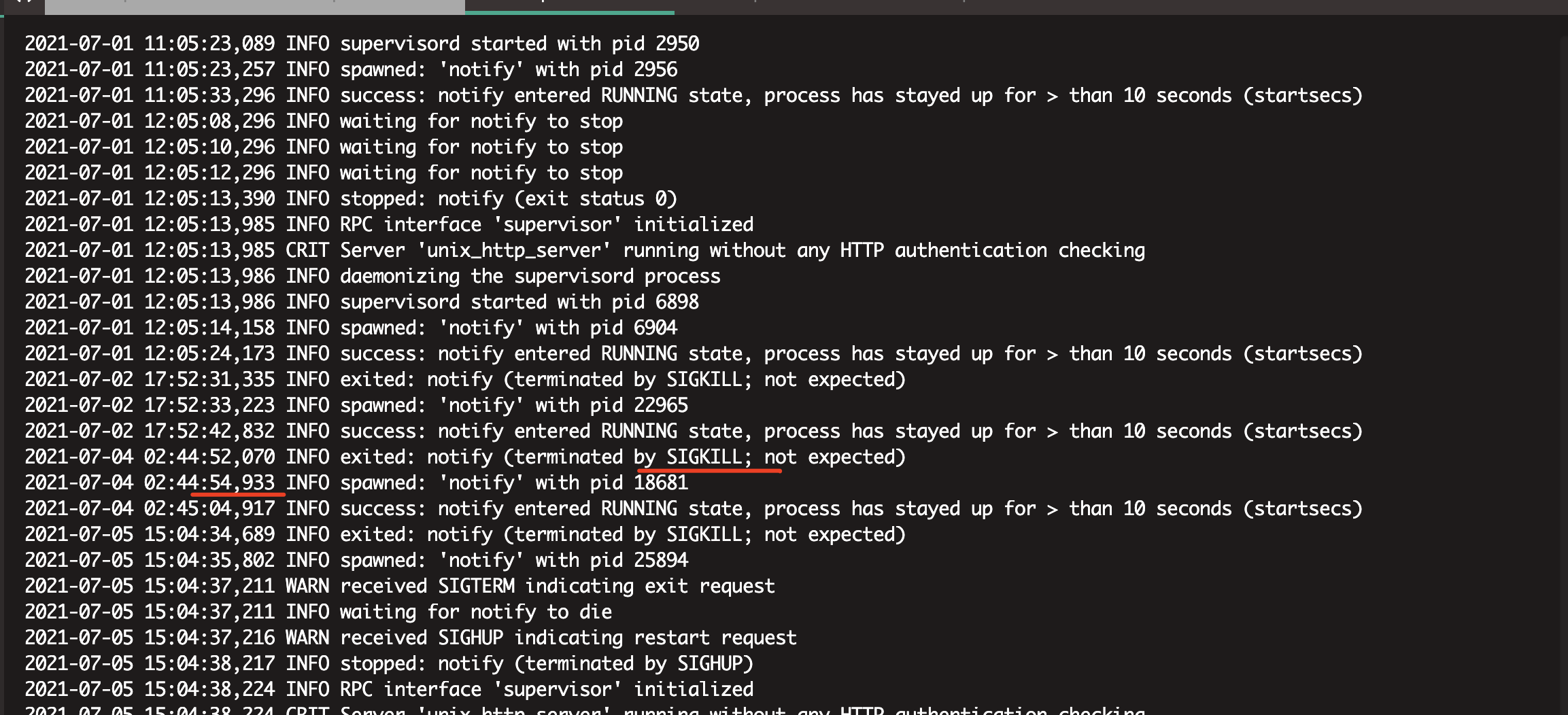
alloc的pprof文件定位到问题函数
重启服务器和服务后,获取内存的pprof文件 //附录2
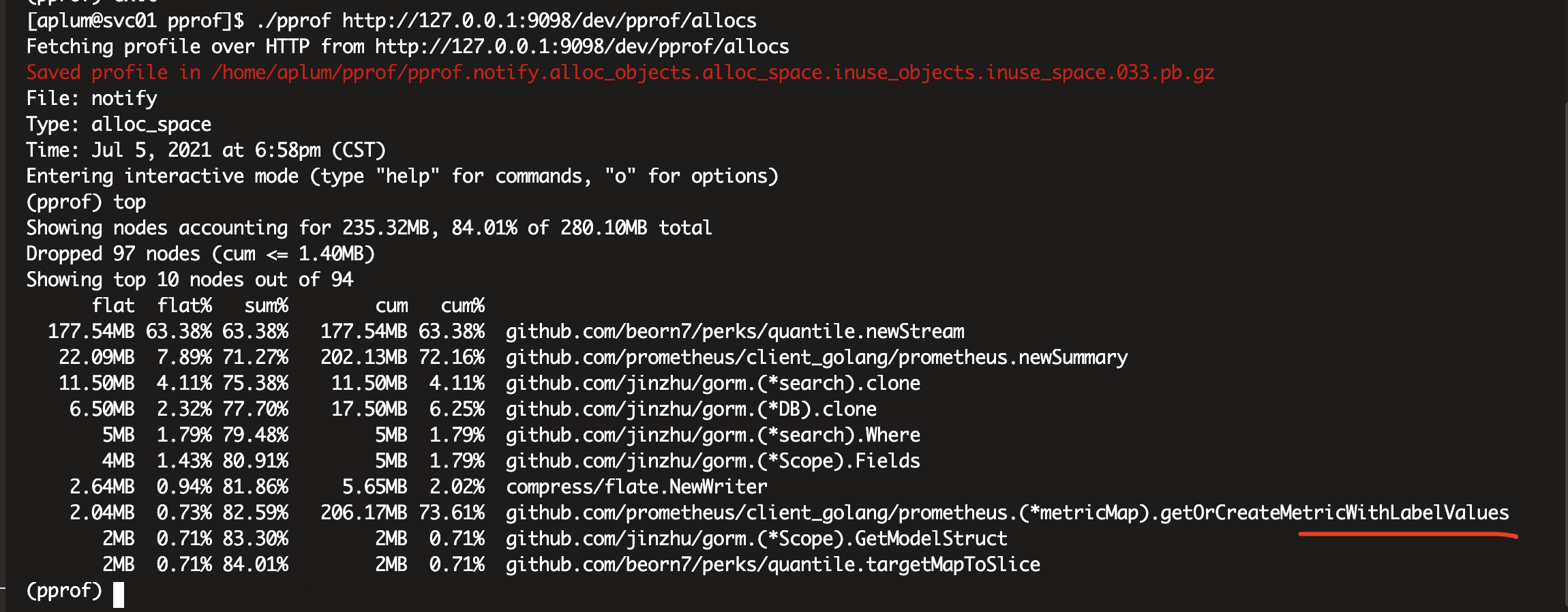
查看源码定位到原因是prometheus的metric无限增加,导致内存增加.
指标中包含了uid,这就导致每个用户都需要生成一个metric。
业务代码示意如下
1.gin通过中间件使用prometheus
r := gin.New()
// middlewares: first use, first execute
r.Use(gin.Recovery())
r.Use(middlewares.PromMiddleware(&middlewares.PromOpts{ // 一个离职的同事写的
IncludeEndpoint: "/api",
}))
r.GET("/metrics", middlewares.PromHandler(promhttp.Handler()))
// ...
msgCenterGroup := r.Group("/api/user/:uid/message", e.msgCenterHdl.ExtractUserID) // 一个新同事写的,也是后续导致问题的地方
2.prometheus中间件:PromMiddleware
// PromMiddleware returns a gin.HandlerFunc for exporting some Web metrics
func PromMiddleware(promOpts *PromOpts) gin.HandlerFunc {
// make sure promOpts is not nil
if promOpts == nil {
promOpts = defaultPromOpts
}
return func(c *gin.Context) {
start := time.Now()
c.Next()
status := fmt.Sprintf("%d", c.Writer.Status())
endpoint := c.Request.URL.Path // 问题在这里,指标取了URL,URL如果是"/api/user/:uid/message",那就是每个用户一个监控指标
method := c.Request.Method
lvs := []string{status, endpoint, method}
if !promOpts.checkIncludeLabel(endpoint, promOpts.IncludeEndpoint) {
return
}
reqDuration.WithLabelValues(lvs...).Observe(time.Since(start).Seconds())
}
}
3.进入三方库代码
// WithLabelValues works as GetMetricWithLabelValues, but panics where
// GetMetricWithLabelValues would have returned an error. Not returning an
// error allows shortcuts like
// myVec.WithLabelValues("404", "GET").Observe(42.21)
func (v *HistogramVec) WithLabelValues(lvs ...string) Observer {
h, err := v.GetMetricWithLabelValues(lvs...)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
return h
}
func (v *HistogramVec) GetMetricWithLabelValues(lvs ...string) (Observer, error) {
metric, err := v.metricVec.getMetricWithLabelValues(lvs...)
if metric != nil {
return metric.(Observer), err
}
return nil, err
}
func (m *metricVec) getMetricWithLabelValues(lvs ...string) (Metric, error) {
h, err := m.hashLabelValues(lvs)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return m.metricMap.getOrCreateMetricWithLabelValues(h, lvs, m.curry), nil
}
// getOrCreateMetricWithLabelValues retrieves the metric by hash and label value
// or creates it and returns the new one.
//
// This function holds the mutex.
func (m *metricMap) getOrCreateMetricWithLabelValues(
hash uint64, lvs []string, curry []curriedLabelValue,
) Metric {
m.mtx.RLock()
metric, ok := m.getMetricWithHashAndLabelValues(hash, lvs, curry)
m.mtx.RUnlock()
if ok {
return metric
}
m.mtx.Lock()
defer m.mtx.Unlock()
metric, ok = m.getMetricWithHashAndLabelValues(hash, lvs, curry) // TODO 这里还没细看,看函数名就是根据指标的hash查找指标metric
if !ok {
inlinedLVs := inlineLabelValues(lvs, curry)
metric = m.newMetric(inlinedLVs...)
m.metrics[hash] = append(m.metrics[hash], metricWithLabelValues{values: inlinedLVs, metric: metric}) // 这里不断增加
}
return metric
}
TODO,理论上,通过对alloc的pprof文件执行list getOrCreateMetricWithLabelValues命令,可以定位问题函数中哪一行代码的内存分配情况,
但是,因为线上环境只有二进制文件,没有源代码,所以无法查看。对于这个问题,可以把ppror文件下载到本地,然后再使用list命令结合源代码来分析情况。
因为已经找到原因了,我也就没有继续这么搞。